|
Acetylation Blocks cGAS Activity and Inhibits Self-DNA-Induced AutoimmunityHighlights• Acetylation suppresses cGAS activity
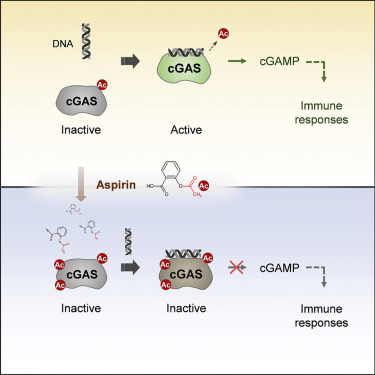
SummaryThe presence of DNA in the cytoplasm is normally a sign of microbial infections and is quickly detected by cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) to elicit anti-infection immune responses. However, chronic activation of cGAS by self-DNA leads to severe autoimmune diseases for which no effective treatment is available yet. Here we report that acetylation inhibits cGAS activation and that the enforced acetylation of cGAS by aspirin robustly suppresses self-DNA-induced autoimmunity. We find that cGAS acetylation on either Lys384, Lys394, or Lys414 contributes to keeping cGAS inactive. cGAS is deacetylated in response to DNA challenges. Importantly, we show that aspirin can directly acetylate cGAS and efficiently inhibit cGAS-mediated immune responses. Finally, we demonstrate that aspirin can effectively suppress self-DNA-induced autoimmunity in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) patient cells and in an AGS mouse model. Thus, our study reveals that acetylation contributes to cGAS activity regulation and provides a potential therapy for treating DNA-mediated autoimmune diseases.
|